Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
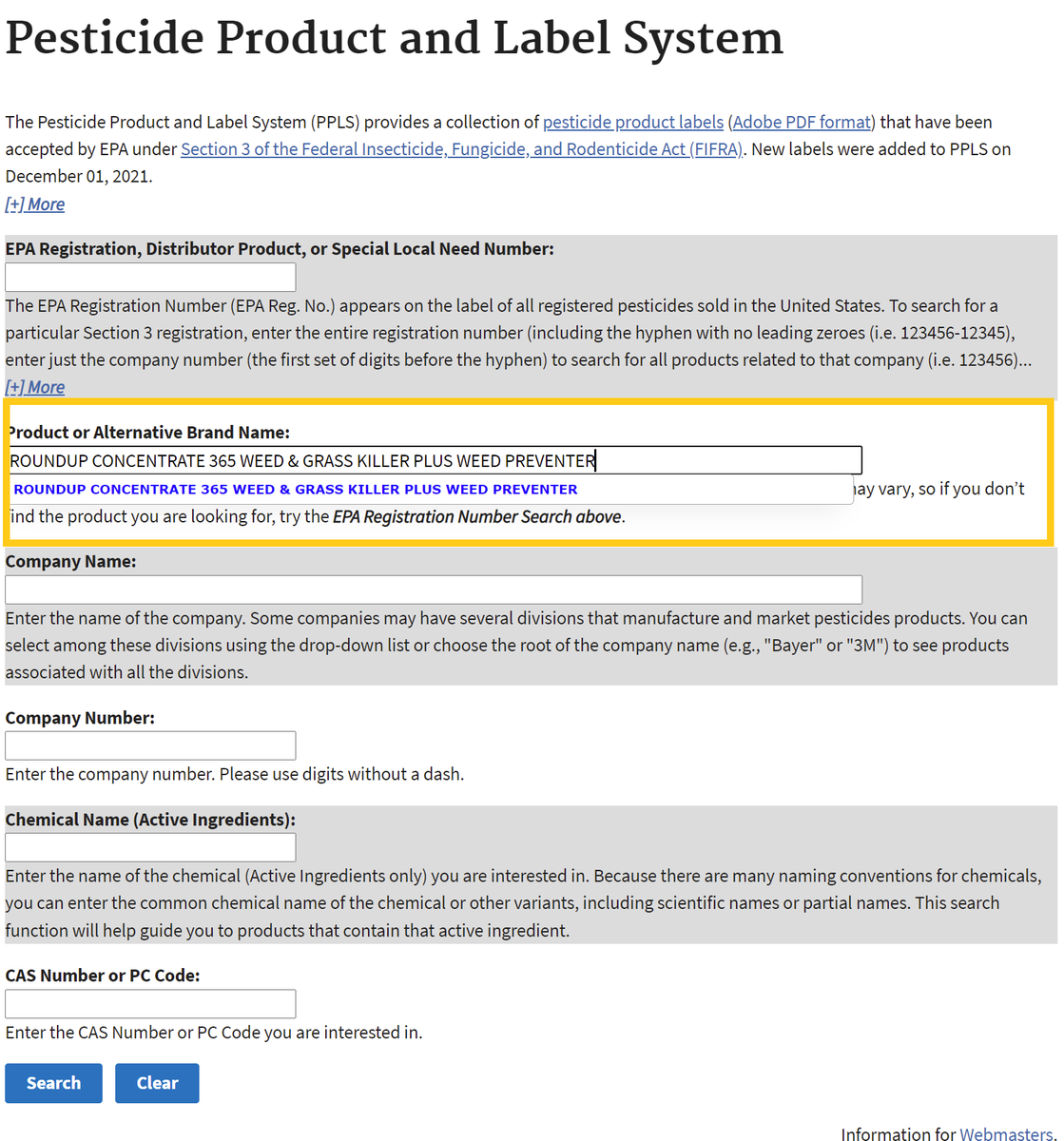
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List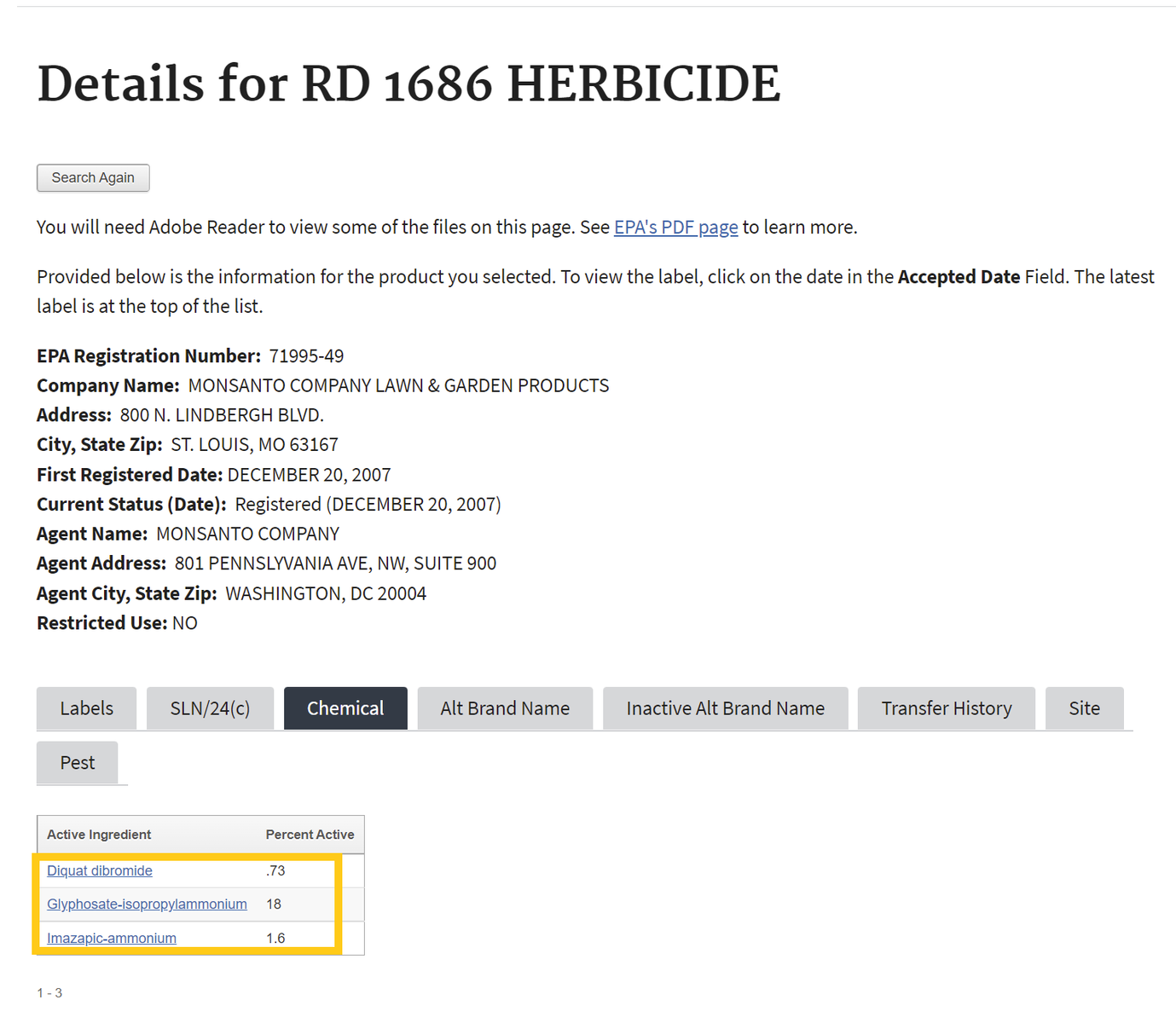
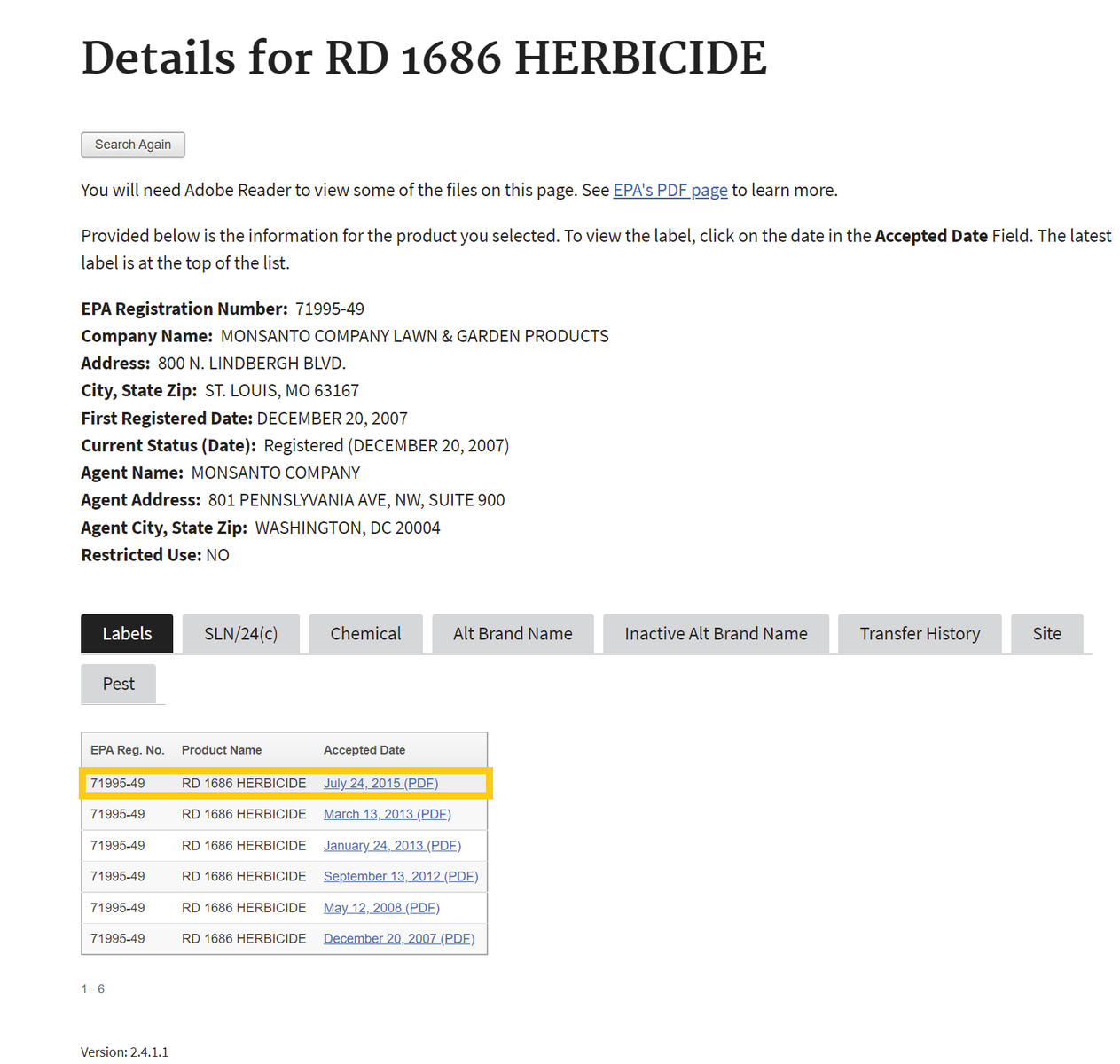
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Triclosan
Updated February 2019
General Information
- Fact Sheet: triclosan-factsheet-3-09.pdf
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Chlorinated phenol biocide
- Uses: Synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent in Consumer products, soaps, deodorants, plastics, toothpastes, etc.
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Suggestive Evidence (1, 2)
- Endocrine Disruption: Yes (3)
- Reproductive Effects: Suggestive Evidence (4, 5)
- Neurotoxicity: Suggestive Evidence (6)
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Not documented
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Yes (3)
- Birth/Developmental: Suggestive Evidence (6, 7)
- Detected in Groundwater: Yes (8, 9)
- Potential Leacher: Not documented
- Toxic to Birds: Not documented
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (3, 10)
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Additional Information
- Regulatory Status:
- FDA Ban for Medical Use in Hospitals (12/2017)
- FDA Ban in Soap Products (9/2016)
- EU Ban for Hygienic Uses (6/2015)
- Regulatory History (2005-2010)
- Supporting information:
- Antibacterials Program Page (Beyond Pesticides)
- Threatened Waters (Beyond Pesticides)
- PAN Pesticides Database: Triclosan (Pesticide Action Network)
- Scorecard Triclosan Factsheet (The Pollution Information Site)
- Studies [compiled from the Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database]
- Antibiotics and common antibacterial biocides stimulate horizontal transfer of resistance at low concentrations.. Jutkina, J., Marathe, N.P., Flach, C.F. and Larsson, D.G.J., 2018. Science of the total Environment, 616, pp.172-178.
- Association between urinary triclosan with bone mass density and osteoporosis in the US adult women, 2005-2010.. Cai, S., Zhu, J., Sun, L., Fan, C., Zhong, Y., Shen, Q. and Li, Y., 2019. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
- Diamondback terrapins as indicator species of persistent organic pollutants: Using Barnegat Bay, New Jersey as a case study. Basile ER, Avery HW, Bien WF, Keller JM. 2011. Chemosphere. 82(1):137-44
- Environmental concentrations of triclosan activate cellular defence mechanism and generate cytotoxicity on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos.. Parenti, CC et al. 2018. Science of the Total Environment 650 (2019): 1752-1758.
- Environmental levels of triclosan and male fertility.. Jurewicz, J et al. 2017. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 25(6), 5484-5490.
- Microbial enzymes induce colitis by reactivating triclosan in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Zhang, J., Walker, M.E., Sanidad, K.Z., Zhang, H., Liang, Y., Zhao, E., Chacon-Vargas, K., Yeliseyev, V., Parsonnet, J., Haggerty, T.D. and Wang, G. Nature communications, 13(1), pp.1-14.
- Anthropogenic Contaminants and Histopathological Findings in Stranded Cetaceans in the Southeastern United States, 2012–2018. Page-Karjian, A., Lo, C.F., Ritchie, B., Harms, C.A., Rotstein, D.S., Han, S., Hassan, S.M., Lehner, A.F., Buchweitz, J.P., Thayer, V.G. and Sullivan, J.M., 2020. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, p.630.
- Cetaceans as bio-indicators revealed the increased risks of triclosan exposure and associated thyroid hormone disruption during the COVID-19 pandemic.. Guo, Y., Shi, W., Liu, Z., Sun, X. and Wu, Y., 2023. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 459, p.132289.
- Thyroid under Attack: The Adverse Impact of Plasticizers, Pesticides, and PFASs on Thyroid Function. Rodrigues, V.G. et al. (2024) Thyroid under Attack: The Adverse Impact of Plasticizers, Pesticides, and PFASs on Thyroid Function, Endocrines. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2673-396X/5/3/32.
Gateway Health and Environmental Effects Citations
1. Yueh, MF et al. 2014. The commonly used antimicrobial additive triclosan is a liver tumor promoter. PNAS doi: 10.1073/pnas.141911911. Triclosan promotes liver cancer cell development and proliferation in mice through pathways common to humans.
2. Lee, HR et al. 2014. Progression of Breast Cancer Cells Was Enhanced by Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals, Triclosan and Octylphenol, via an Estrogen Receptor-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Cellular and Mouse Xenograft Models. Chemical Research in Toxicology doi: 10.1021/tx5000156.
3. Beyond Pesticides ChemWatch Factsheets. (Cited under factsheets on Beyond Pesticides Gateway; see top of individual chemical page)
4. Riad, M et al. 2017. Reproductive toxic impact of subchronic treatment with combined butylparaben and triclosan in weanling male rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol doi: 10.1002/jbt.22037. Treatment with triclosan alone causes testicular oxidative stress and DNA damage, leading to a marked reduction in sperm count and sperm motility.
5. Jurewicz, J et al. 2017. Environmental levels of triclosan and male fertility. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 25(6), 5484-5490. Men with higher urinary concentrations of triclosan have poorer semen quality, exhibiting a greater percentage of sperm with abnormal morphology as compared to men with lower triclosan levels.
6. Kim, J et al. 2017. Triclosan affects axon formation in the neural development stages of zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Environmental Pollution doi: 10.1016/j.enjvpol.2017.12.110.
7. Lassen et al. 2016. Prenatal Triclosan Exposure and Anthropometric Measures Including Anogenital Distance in Danish Infants. Environmental Health Perspectives doi: 10.1289/ehp.1409637. Prenatal triclosan exposure associated with reduced head circumference, a trait linked to cognitive impairment.
8. Stuart, M et al. 2012. Review of risk from potential emerging contaminants in UK groundwater. Science of the Total Environment 416, 1-21. UK Environment Agency detected triclosan in groundwater 22 times in 22 sites over the period 1992-2009, at a maximum concentration of 2.11 µg/L.
9. Karnjanapiboonwong, A et al. 2011. Occurrence of PPCPs at a Wastewater Treatment Plant and in Soil and Groundwater at a Land Application Site. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 216(1-4), 257-273. Triclosan detected in 5 out of 7 groundwater samples from a West Texas Land Application Site, at concentrations ranging 12-53 ng/L.
10. Parenti, CC et al. 2018. Environmental concentrations of triclosan activate cellular defence mechanism and generate cytotoxicity on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Science of the Total Environment 650, 1752-1758. Triclosan levels commonly found in the environment invoke oxidative stress immune responses and cause high levels of cell death in zebrafish embryos.








.png)


