Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
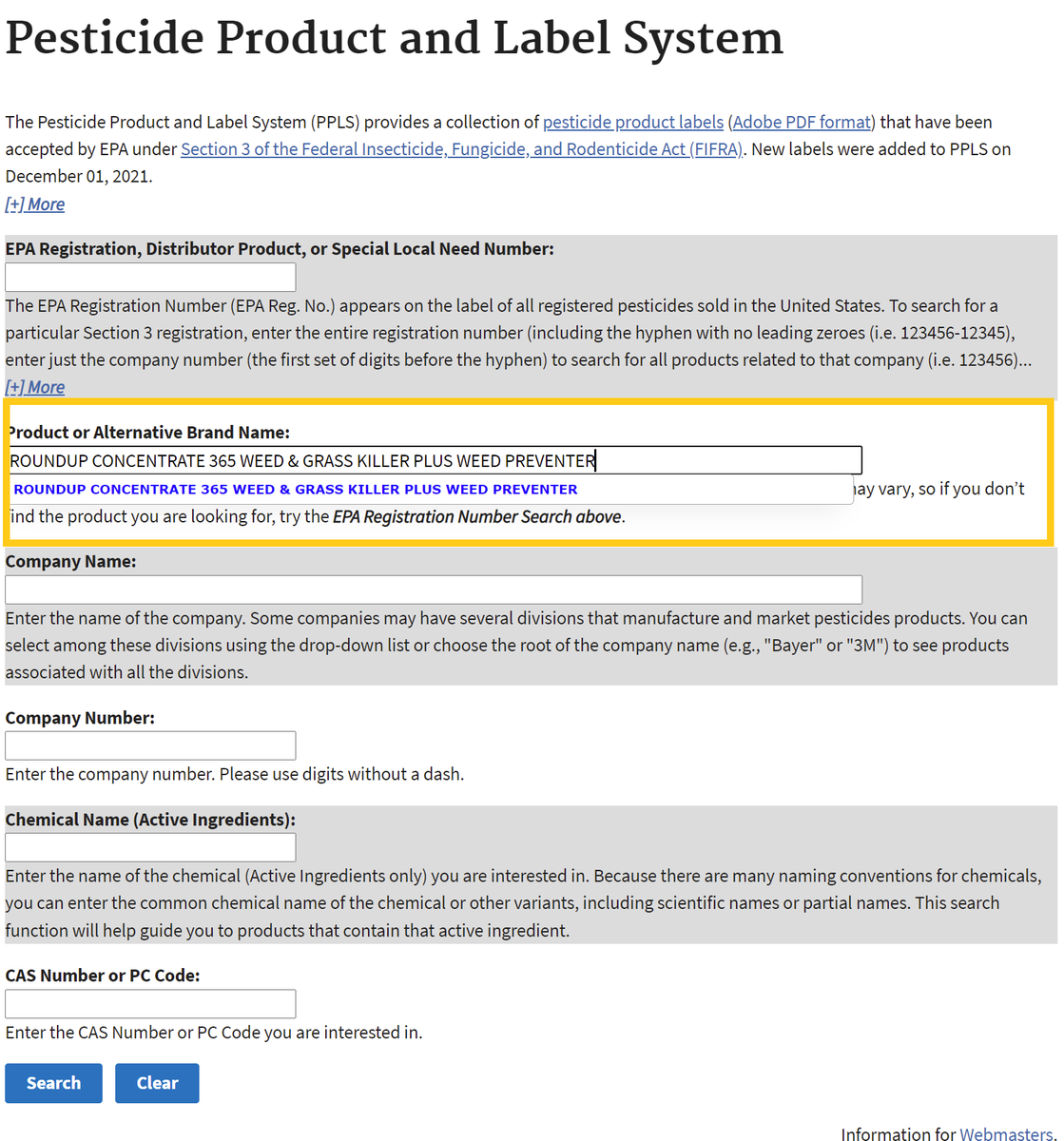
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List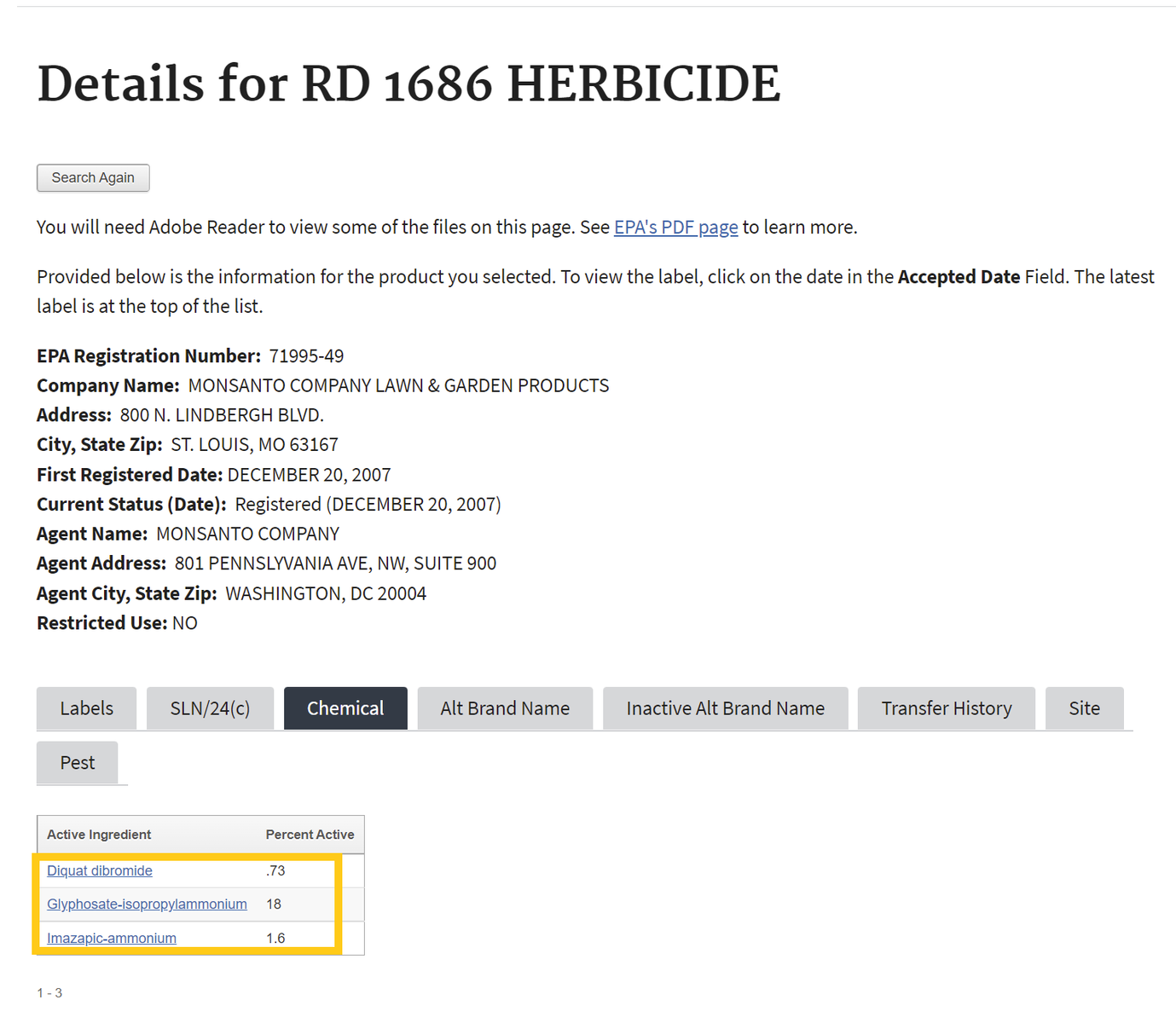
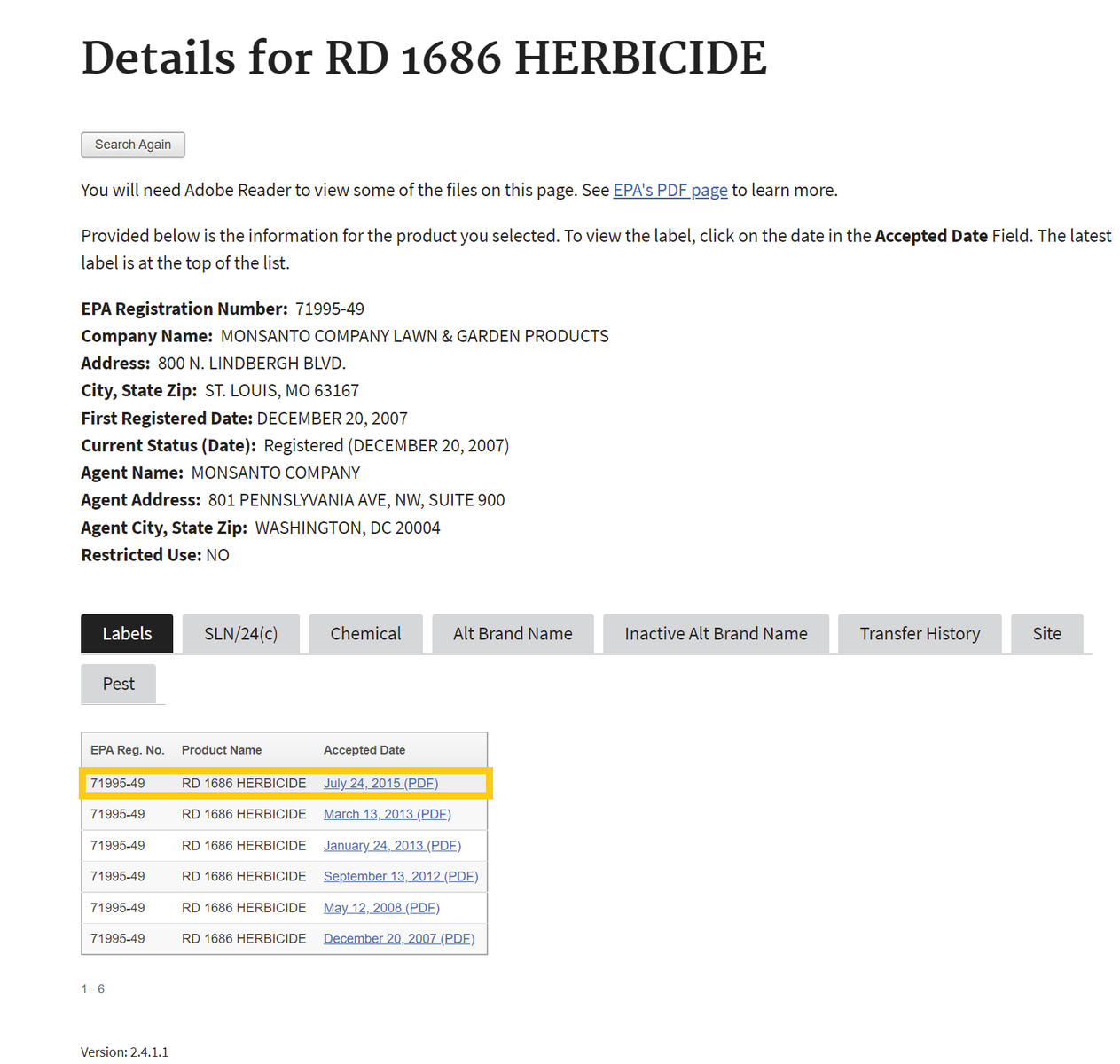
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Hexachlorobenzene
General Information
- Uses: Hexachlorobenzene was previously used as a pesticide, fungicide, and wood preservative, and in the production of synthetic rubber, dyes, and pyrotechnic materials. While not approved for use anymore, it is now primarily a byproduct of other chemical manufacturing processes.
- Alternatives: Organic Agriculture
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Yes (1)
- Endocrine Disruption: Not documented
- Reproductive Effects: Yes (1)
- Neurotoxicity: Yes (1)
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Yes (1)
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Yes (1)
- Birth/Developmental: Yes (1)
- Detected in Groundwater: Not documented
- Potential Leacher: Not documented
- Toxic to Birds: Not documented
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (2)
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Additional Information
- Regulatory Status:
- Supporting information:
- PAN Pesticides Database: Hexachlorobenzene (Pesticide Action Network)
- Extension Toxicology Network Pesticide Profile
- CDC Toxic Substances Portal
- Studies [compiled from the Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database]
- Chronic kidney disease from agricultural communities—association and accumulation of hexachlorobenzene, malathion, and parathion pesticides. Verma, J. et al. (2024) Chronic kidney disease from agricultural communities-association and accumulation of hexachlorobenzene, malathion, and parathion pesticides, Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13530-024-00222-y.
- Status of pesticides pollution in Tanzania – A review. Elibariki, R., & Maguta, M. M. (2017). Status of pesticides pollution in Tanzania - A review. Chemosphere, 178, 154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.036
- Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Debler, F., Gandrass, J., Paul Ramacher, M. O., Koenig, A. M., Zimmermann, S., & Joerss, H. (2025). Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 373, 126175. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126175
- The potential endocrine-disrupting of fluorinated pesticides and molecular mechanism of EDPs in cell models . Liu, Y. et al. (2025) The potential endocrine-disrupting of fluorinated pesticides and molecular mechanism of EDPs in cell models, Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0147651324016919.
- The mode of action of different organochlorine pesticides families in mammalians. Baratzhanova, G. et al. (2024) The mode of action of different organochlorine pesticides families in mammalians, Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1382668924001546?via%3Dihub.
- Exposure to pesticides, persistent and non − persistent pollutants in French 3.5-year-old children: Findings from comprehensive hair analysis in the ELFE national birth cohort. Macheka, L. et al. (2024) Exposure to pesticides, persistent and non − persistent pollutants in French 3.5-year-old children: Findings from comprehensive hair analysis in the ELFE national birth cohort, Environment International. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412024004677.
- Persistent organic pollutants and the size of ovarian reserve in reproductive-aged women. Björvang, R.D., Hassan, J., Stefopoulou, M., Gemzell-Danielsson, K., Pedrelli, M., Kiviranta, H., Rantakokko, P., Ruokojärvi, P., Lindh, C.H., Acharya, G. and Damdimopoulou, P. Environment International, 155, p.106589.
- Correlates of organochlorine pesticide plasma concentrations among reproductive-aged black women. Orta, O.R., Wesselink, A.K., Bethea, T.N., Henn, B.C., Sjödin, A., Wegienka, G., Baird, D.D. and Wise, L.A., 2020. Environmental Research, p.109352.
- Airborne Pesticides from Agricultural Practices: A Critical Review of Pathways, Influencing Factors, and Human Health Implications. Boonupara, T., Udomkun, P., Khan, E., & Kajitvichyanukul, P. (2023). Airborne Pesticides from Agricultural Practices: A Critical Review of Pathways, Influencing Factors, and Human Health Implications. Toxics, 11(10), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100858
Gateway Health and Environmental Effects Citations
1. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. ToxFAQs. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxfaqs/index.asp.
2. National Library of Medicine. PubChem Hazardous Substances Database. PubChem (nih.gov)








.png)


