Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
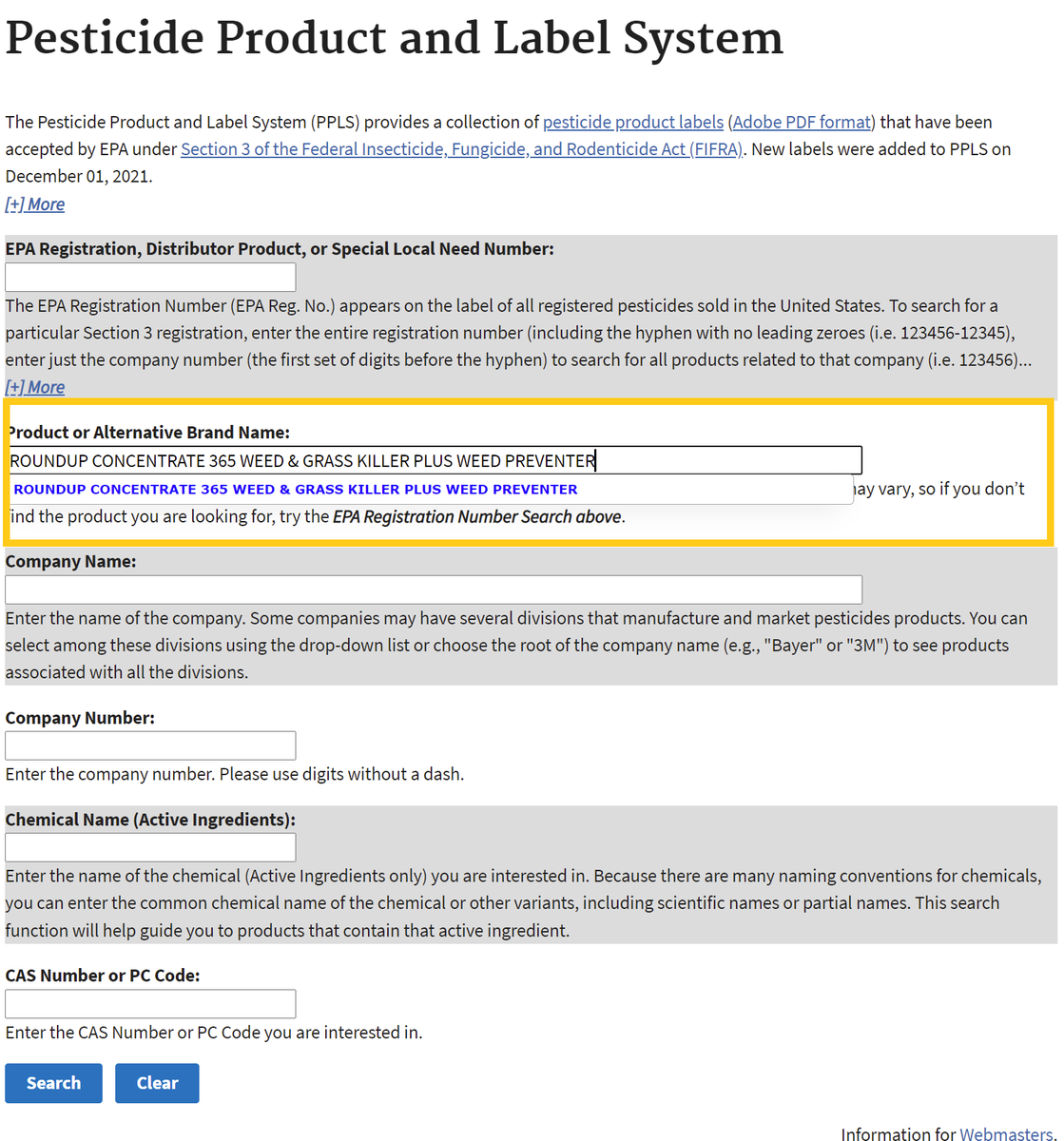
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List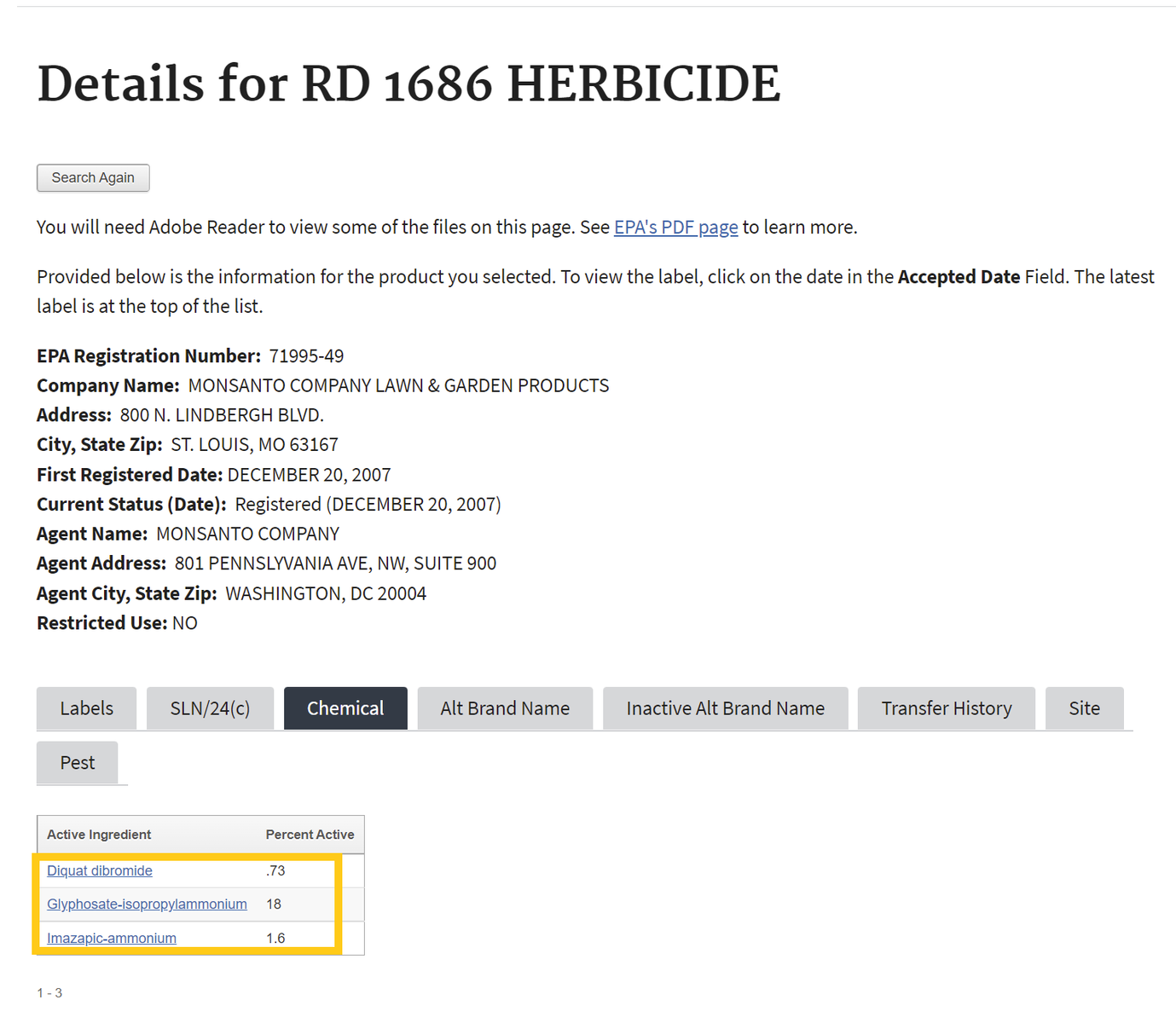
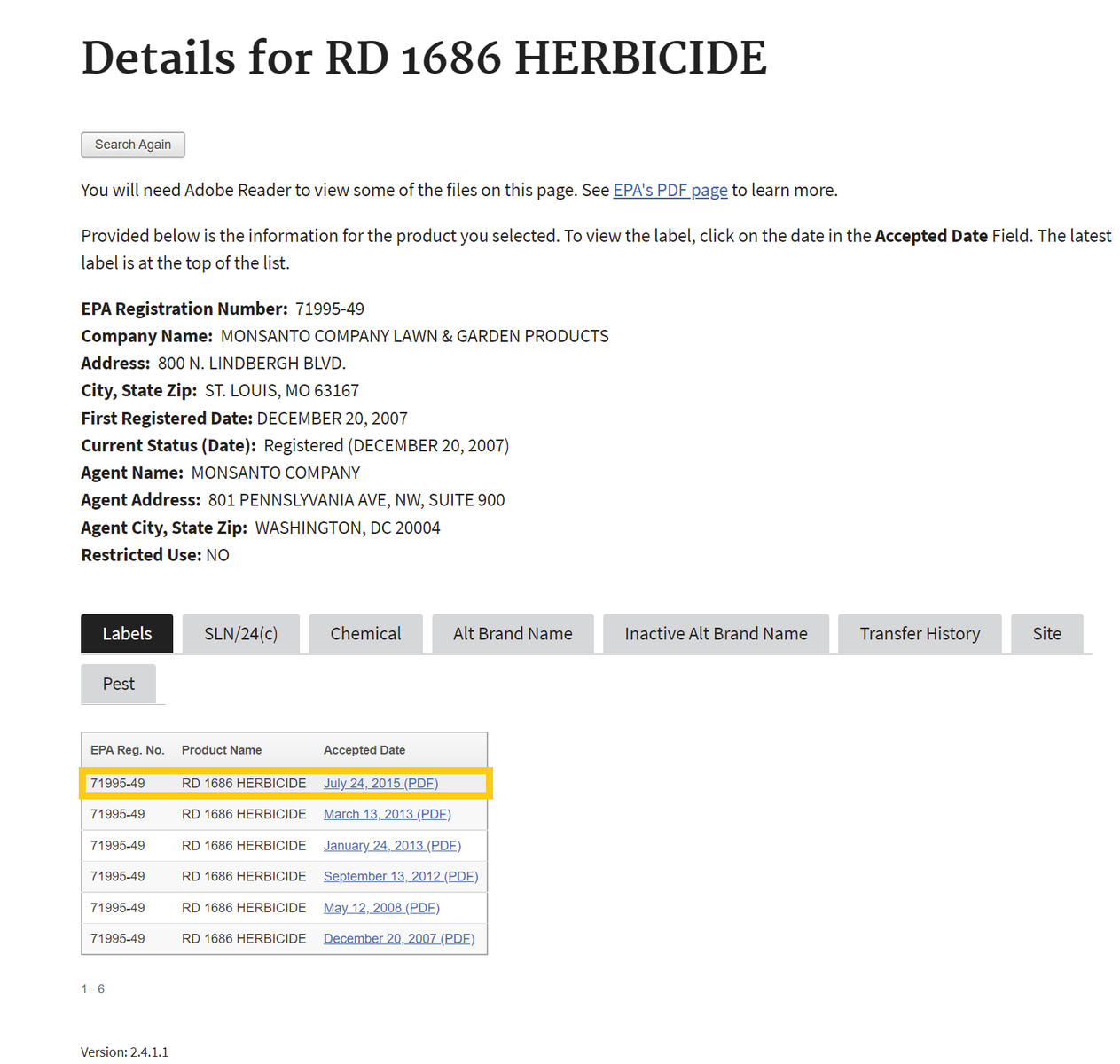
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Pyriproxyfen
General Information
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Unclassified
- Uses: Agriculture, structural pest control
- Alternatives: Organic agriculture, Organic lawn care
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Insufficiently Studied
- Endocrine Disruption: Likely (1, 2)
- Reproductive Effects: Likely (3, 4)
- Neurotoxicity: Possible (5)
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Yes (6)
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Not Likely
- Birth/Developmental: Likely (4, 5)
- Detected in Groundwater: Low (7)
- Potential Leacher: Parent = Slight; Metabolite = Yes (8)
- Toxic to Birds: Possible (9)
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (10, 2)
- Toxic to Bees: Yes (11, 12, 13)
Residential Uses as Found in the ManageSafe™ Database
Additional Information
- Supporting information:
- Studies [compiled from the Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database]
- Fate of pyriproxyfen in soils and plants. Devillers, J., 2020. Toxics, 8(1), p.20.
- Determination by chromatography and cytotoxotoxic and oxidative effects of pyriproxyfen and pyridalyl. de Oliveira, M.D.D.A., de Almeida, P.M., Martins, F.A., Cavalcante, A.A.D.C.M., dos Santos, T.D.J.A., Feitosa, C.M., Rai, M., dos Reis, A.C. and da Costa Júnior, J.S., 2019. Chemosphere, 224, pp.398-406.
- The enantioselective environmental behavior and toxicological effects of pyriproxyfen in soil. Liu, H., Yi, X., Bi, J., Wang, P., Liu, D. and Zhou, Z., 2019. Journal of hazardous materials, 365, pp.97-106.
- The pyriproxyfen metabolite, 4′–OH–PPF, disrupts thyroid hormone signaling in neural stem cells, modifying neurodevelopmental genes affected by ZIKA virus infection. Vancamp, P., Spirhanzlova, P., Sébillot, A., Butruille, L., Gothié, J.D., Le Mével, S., Leemans, M., Wejaphikul, K., Meima, M., Mughal, B.B. and Roques, P. Environmental Pollution, 285, p.117654.
- The potential endocrine disruption of pesticide transformation products (TPs): The blind spot of pesticide risk assessment. Ji, C., Song, Q., Chen, Y., Zhou, Z., Wang, P., Liu, J., Sun, Z., & Zhao, M. (2020). The potential endocrine disruption of pesticide transformation products (TPs): The blind spot of pesticide risk assessment. Environment international, 137, 105490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105490
Gateway Health and Environmental Effects Citations
1. Ji, C., Song, Q., Chen, Y., Zhou, Z., Wang, P., Liu, J., Sun, Z. and Zhao, M., 2020. The potential endocrine disruption of pesticide transformation products (TPs): The blind spot of pesticide risk assessment. Environment international, 137, p.105490. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412019332647?via%3Dihub#s0120
2. Devillers, J., 2020. Fate and ecotoxicological effects of pyriproxyfen in aquatic ecosystems. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(14), pp.16052-16068. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32180143/
3. Shahid, A., Zaidi, S.D.E.S., Akbar, H. and Saeed, S., 2019. An investigation on some toxic effects of pyriproxyfen in adult male mice. Iranian journal of basic medical sciences, 22(9), p.997. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6880530/
4. Shahid, A. and Saher, M., 2020. Repeated exposure of pyriproxyfen to pregnant female mice causes developmental abnormalities in prenatal pups. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, pp.26998-27009. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32382916/
5. Truong, L., Gonnerman, G., Simonich, M.T. and Tanguay, R.L., 2016. Assessment of the developmental and neurotoxicity of the mosquito control larvicide, pyriproxyfen, using embryonic zebrafish. Environmental pollution, 218, pp.1089-1093. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0269749116309794
7. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Arena, M., Auteri, D., Barmaz, S., Brancato, A., Brocca, D., Bura, L., Carrasco Cabrera, L., Chiusolo, A., Court Marques, D. and Crivellente, F., 2018. Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance spinosad. EFSA Journal, 16(5), p.e05252. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7009054/
8. Devillers, J., 2020. Fate of pyriproxyfen in soils and plants. Toxics, 8(1), p.20. https://www.mdpi.com/2305-6304/8/1/20/htm
9. The University of Hertfordshire. 2021. Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB): Pyriproxyfen. https://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/574.htm
10. Pesticide Action Network Pesticide Database. http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Search_Chemicals.jsp.
11. Chen, Y.W., Wu, P.S., Yang, E.C., Nai, Y.S. and Huang, Z.Y., 2016. The impact of pyriproxyfen on the development of honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) colony in field. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 19(3), pp.589-594. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1226861516300012
12. Fourrier, J., Deschamps, M., Droin, L., Alaux, C., Fortini, D., Beslay, D., Le Conte, Y., Devillers, J., Aupinel, P. and Decourtye, A., 2015. Larval exposure to the juvenile hormone analog pyriproxyfen disrupts acceptance of and social behavior performance in adult honeybees. PloS one, 10(7), p.e0132985. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0132985
13. Devillers, J. and Devillers, H., 2020. Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Pyriproxyfen on Apis and Non-Apis Bees. Toxics, 8(4), p.104. https://www.mdpi.com/2305-6304/8/4/104








.png)


