Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
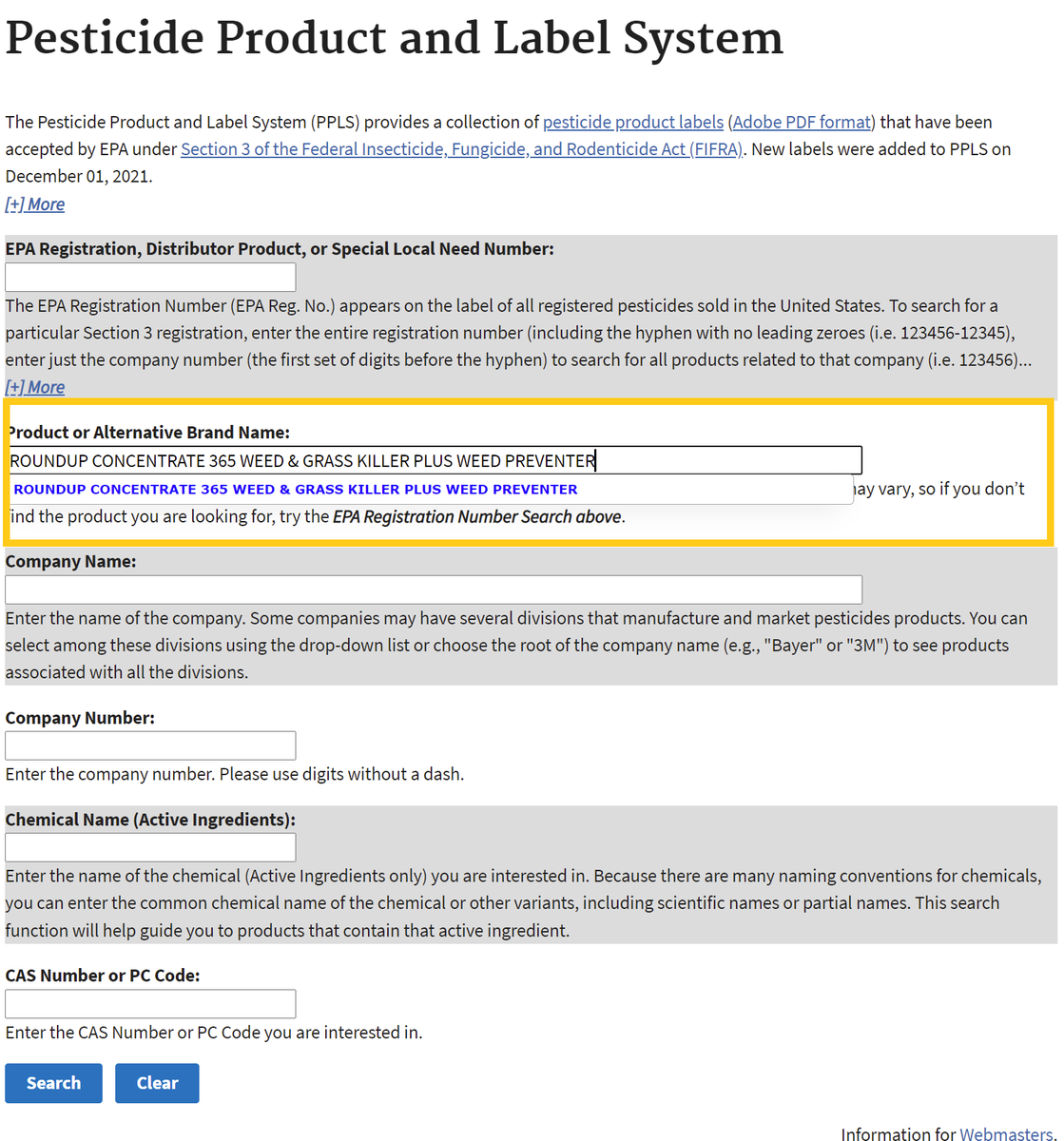
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List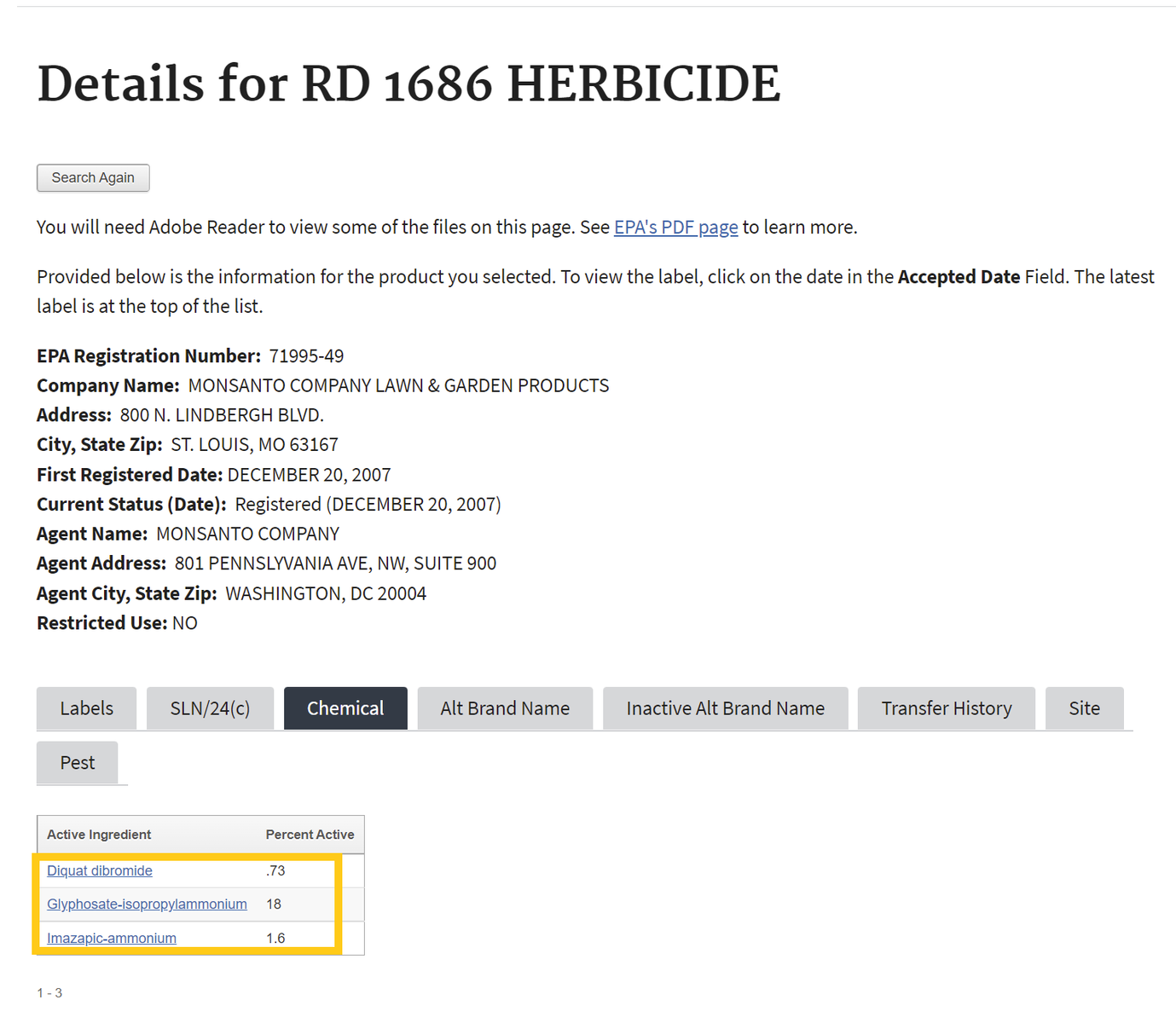
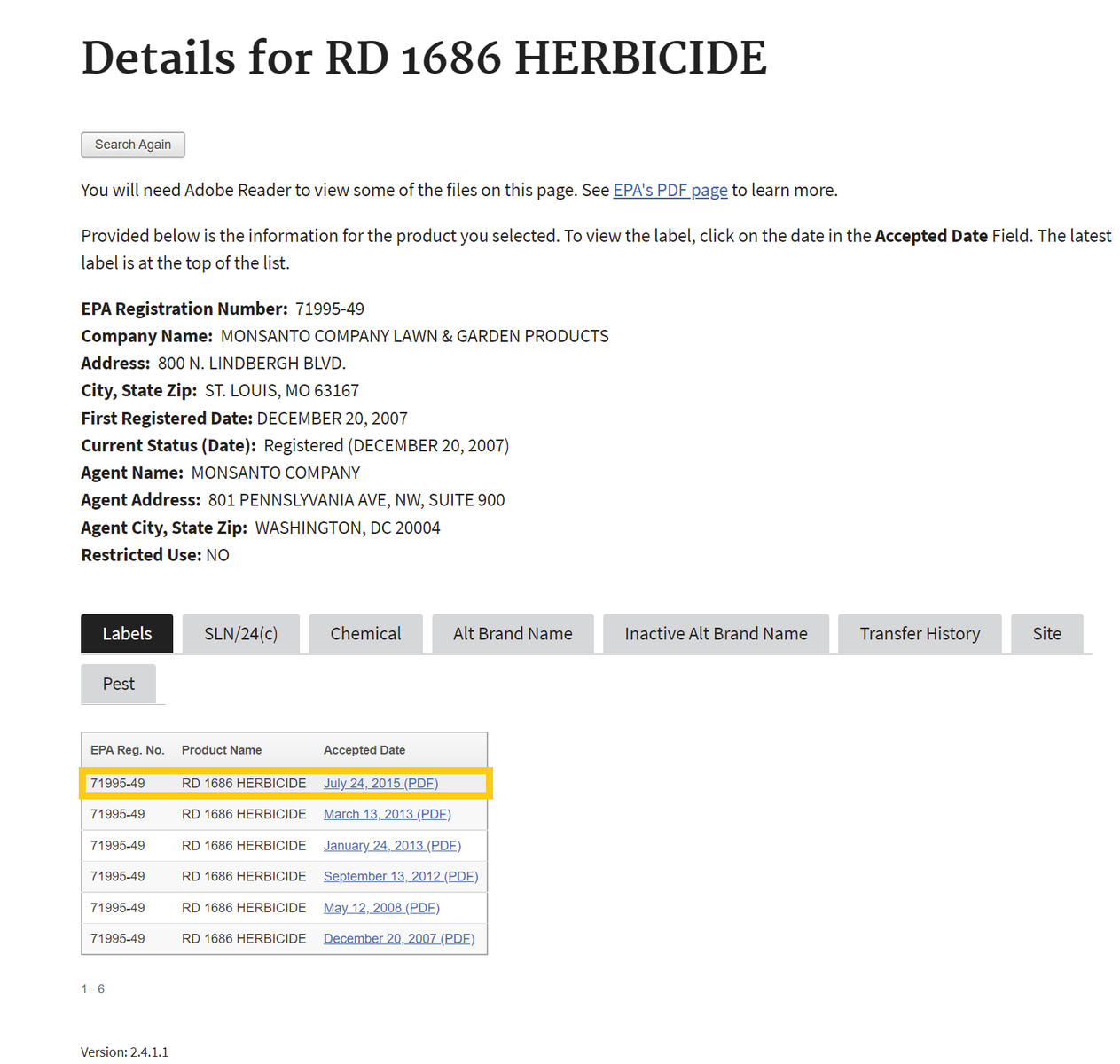
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Trifluralin
Updated February 2019
General Information
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Dinitroaniline compound herbicide
- Uses: Annual grasses and broadleaf weeds on a variety of food crops and non-food uses, including residential use site
- Alternatives: Organic agriculture, Least toxic-weed managment
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Yes (66, 67, 68, 69)
- Endocrine Disruption: Probable (5, 36)
- Reproductive Effects: Yes (8)
- Neurotoxicity: Not documented
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Yes (4)
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Yes (8)
- Birth/Developmental: Not documented
- Detected in Groundwater: Yes (37)
- Potential Leacher: Not documented
- Toxic to Birds: Not documented
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (8)
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Residential Uses as Found in the ManageSafe™ Database
Additional Information
- Supporting information:
- Extoxnet Trifluralin Factsheet (Extension Toxicology Network)
- PAN Pesticides Database:Trifluralin (Pesticide Action Network)
- Scorecard Trifluralin Factsheet (The Pollution Information Site)
- FAN Trifluralin Factsheet (Fluoride Action Network)
- Studies:
- Agricultural exposures and gastric cancer risk in Hispanic farm workers in California. Mills, P.K., and Yang, R.C. 2007. Environ Res 104(2):282-289.
- Assessment of genetic effects and pesticide exposure of farmers in NW Greece. Moshou, H., Karakitsou, A., Yfanti, F., Hela, D., Vlastos, D., Paschalidou, A.K., Kassomenos, P. and Petrou, I., 2020. Environmental Research, p.109558.
- Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to trifluralin in the Agricultural Health Study. . Kang, D. et al., 2008. Environmental research, 107(2), pp.271-276.
- Human exposure and risk assessment to airborne pesticides in a rural French community.. Coscollà C, López A, Yahyaoui A, Colin P, et al. 2017. Sci Total Environ. 584-585:856-868
- In vitro genotoxicity assessment of dinitroaniline herbicides pendimethalin and trifluralin.. Kılıç, Z.S., Aydın, S., Bucurgat, Ü.Ü. and Başaran, N., 2018. Food and chemical toxicology, 113, pp.90-98.
- A pesticide and iPSC dopaminergic neuron screen identifies and classifies Parkinson-relevant pesticides. Paul, K.C., Krolewski, R.C., Lucumi Moreno, E., Blank, J., Holton, K.M., Ahfeldt, T., Furlong, M., Yu, Y., Cockburn, M., Thompson, L.K. and Kreymerman, A., 2023. Nature Communications, 14(1), p.2803.
- Pesticide use and incident Parkinson’s disease in a cohort of farmers and their spouses. Shrestha, S. et al. (2020) Pesticide use and incident parkinson’s disease in a cohort of farmers and their spouses, Environmental research. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7822498/.
- Pesticides and prostate cancer incidence and mortality: An environment-wide association study. Soerensen, S. et al. (2024) Pesticides and prostate cancer incidence and mortality: An environment-wide association study, Cancer. Available at: https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.35572.
- Pesticide exposure and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Zago, A. M., Faria, N. M. X., Fávero, J. L., Meucci, R. D., Woskie, S., & Fassa, A. G. (2022). Pesticide exposure and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Global public health, 17(12), 3944–3966. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2020.1808693
- Association between pesticide exposure and colorectal cancer risk and incidence: A systematic review. Matich, E. K., Laryea, J. A., Seely, K. A., Stahr, S., Su, L. J., & Hsu, P. C. (2021). Association between pesticide exposure and colorectal cancer risk and incidence: A systematic review. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 219, 112327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112327








.png)


